What is the difference between SCADA system and DCS system in automated factories
In the field of industrial automation, SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System) and DCS (Distributed Control System) are two common systems. Although they are both used for monitoring and controlling industrial processes, they have some significant differences in system composition, functionality, and applications.
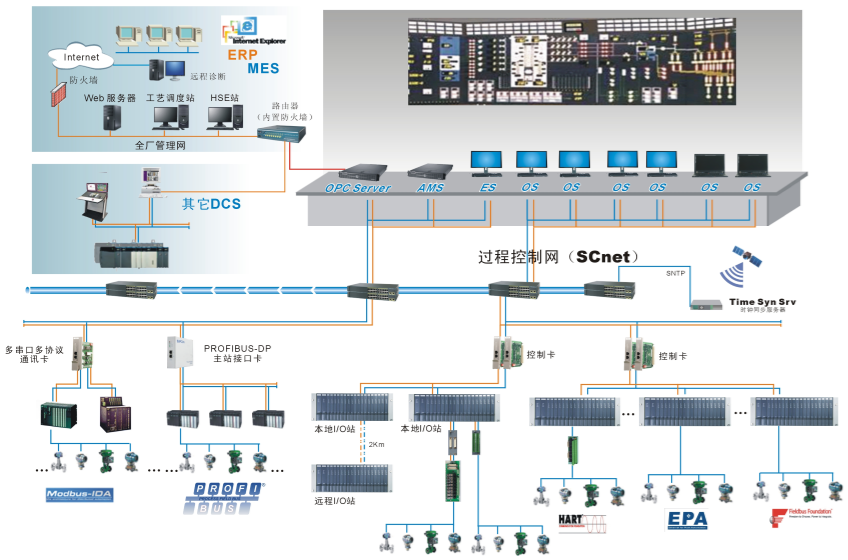
1. Composition of SCADA system
Firstly, the SCADA system mainly consists of the following parts:
1. Human Machine Interface (HMI): Provides an interactive interface between the operator and the system for displaying program status, monitoring, and controlling programs.
2. Computer monitoring system: responsible for data collection, storage, and processing, as well as sending control instructions to remote devices.
3. Remote terminal control system or programmable logic controller (PLC): deployed at remote sites, responsible for connecting sensors and actuators, collecting on-site data, and executing control instructions.
4. Communication network: Provides data transmission channels to ensure real-time communication between monitoring systems and remote devices.
2. Composition of DCS system
In contrast, DCS systems typically include:
Process input/output interface: used to connect and convert various signals in process control.
Process control unit: executes control algorithms and logic to achieve precise process control.
Operator Station: Provides an operator interface for monitoring and controlling the entire production process.
Data high-speed channel: Ensure high-speed data transmission between various components of the system.
Management computer: used for system management and configuration.
In terms of functionality and application, SCADA focuses more on remote monitoring and data acquisition, and is suitable for wide area distributed monitoring systems. DCS emphasizes precise control of industrial processes and is suitable for large and complex industrial facilities.